Picture-in-Picture (PiP)
Overview
The Picture-in-Picture feature allows you to watch a stream in a floating window that is always on top of other apps or windows.
Transitioning the player to a PiP window can be done in two ways:
- Explicitly, using the player API
- Automatically, when transitioning to background in mobile apps.
This page describes how to configure PiP with react-native-theoplayer.
Configuration
Transitioning to PiP automatically
The pipConfiguration property that is set on the player instance
allows native mobile apps on iOS and Android to automatically transition into PiP presentation mode when
the app goes to the background. The property can be changed at run-time, allowing to change the
behaviour depending on the active media asset.
player.pipConfiguration = { startsAutomatically: true }
Using presentationMode
The picture-in-picture presentation mode can also be triggered explicitly using the
THEOplayer API:
// Change presentation mode (inline, fullscreen or pip).
player.presentationMode = PresentationMode.pip;
Listening for presentationMode changes
Each time the player transitions from one presentationMode to another, either automatically
or manually through the API, the player dispatches a presentationmodechange event that can be
used to update the user-interface.
player.addEventListener(
PlayerEventType.PRESENTATIONMODE_CHANGE,
(event: PresentationModeChangeEvent) => {
const newPresentationMode = event.presentationMode;
}
);
Additional configuration is necessary depending on the platform the app runs on.
Android
Picture-in-picture support for Android was added in Android 8.0 (API level 26).
A react-native app on Android is typically a single-activity application. Launching picture-in-picture mode means the whole activity transitions to an out-of-app PiP window.
Enabling PiP support
To enable PiP support, make sure to set android:supportsPictureInPicture=true in the
app's manifest, and specify that the activity handles layout configuration changes
so that it does not relaunch when layout changes occur during PiP mode transitions.
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:configChanges="screenSize|smallestScreenSize|screenLayout|orientation"
android:supportsPictureInPicture="true">
</activity>
Also, add these methods to the MainActivity to let react-native know
when the app makes PiP, background and foreground transitions:
public override fun onUserLeaveHint() {
// Notify the app is backgrounded in case the user taps home or back, and
// the app needs to transition to PiP automatically.
this.sendBroadcast(Intent("onUserLeaveHint"))
super.onUserLeaveHint()
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(
isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean,
newConfig: Configuration
) {
// Notify that the app is changing its picture-in-picture mode.
super.onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode, newConfig)
val intent = Intent("onPictureInPictureModeChanged")
intent.putExtra("isInPictureInPictureMode", isInPictureInPictureMode)
this.sendBroadcast(intent)
}
PiP controls
The PiP window will show the default controls to configure, maximize and close the PiP window. In addition, the active media session enables a play/pause toggle button and (disabled) play-list navigator buttons.
 |  | 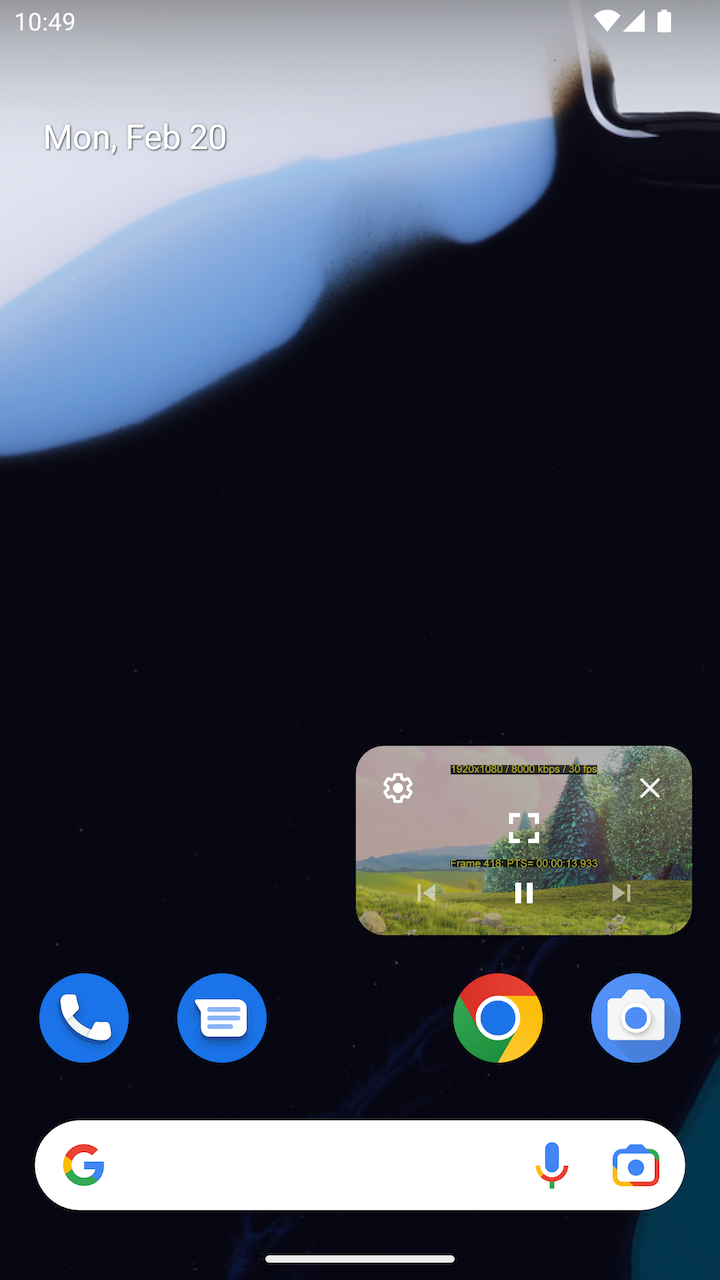 |
|---|
User interface
As mentioned before, when choosing picture-in-picture
presentation mode on Android the whole activity moves to the PiP window, including the
react-native UI that potentially lies on top. For this reason it is necessary to disable the UI
on Android in PiP mode, as opposed to iOS and web where the video view is separated from the rest
More information on Android PiP support can be found on the Android developer pages.
iOS
No extra configuration is necessary to support picture-in-picture on iOS.
In contrast to Android, only the video view will move to the floating PiP window. The react-native UI can remain visible and provide playback control.
Web
On web the behavior is similar to iOS, where PiP can be started manually from the UI. It will open up a floating PiP window displaying the video element.